This section shows how annual and seasonal average temperatures in India have changed since 1901.
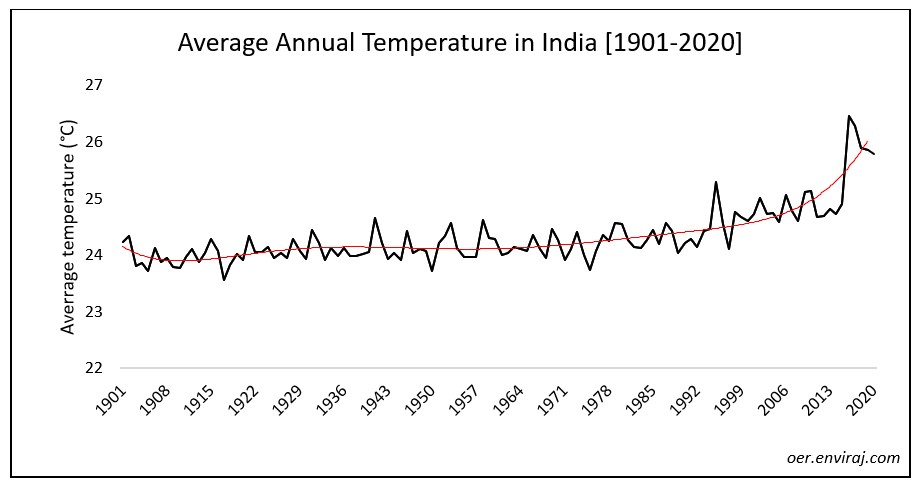
The country’s meteorological department follows the international standard of four seasons with some local adjustments: winter (January and February), summer (March, April and May), Monsoon (rainy) season (June to September), and a post-monsoon period (October to December).
![Average Summer Temperature in India [1901-2020]](https://oer.enviraj.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/summer-1.jpg)
![Average Monsoon Temperature in India [1901-2020]](http://oer.enviraj.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Monsoon.jpg)
![Average Post Monsoon Temperature in India [1901-2020]](http://oer.enviraj.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/post-monsoon.jpg)
![Average Winter Temperature in India [1901-2020]](http://oer.enviraj.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Winter.jpg)
Key Points
- Since 1901, the average surface temperature across the country has risen at an average rate of 0.13°C per decade. Average temperatures have risen more quickly since the mid 1990s (0.26 to 0.56°C per decade since 1995).
- 2016 was the warmest year on record with mean annual temperature 26.45 °C, 2017 was the second-warmest, and 2011–2020 was the warmest decade on record since thermometer-based observations began.
