What is Green Hydrogen?
Green Hydrogen is the hydrogen produced using the renewable energy sources. Green hydrogen is increasingly being viewed as the cleaner alternative for vehicles, ships, airplanes, which has the capability to reduce climate change to a great extent.
Difference Between Grey, Blue and Green hydrogen
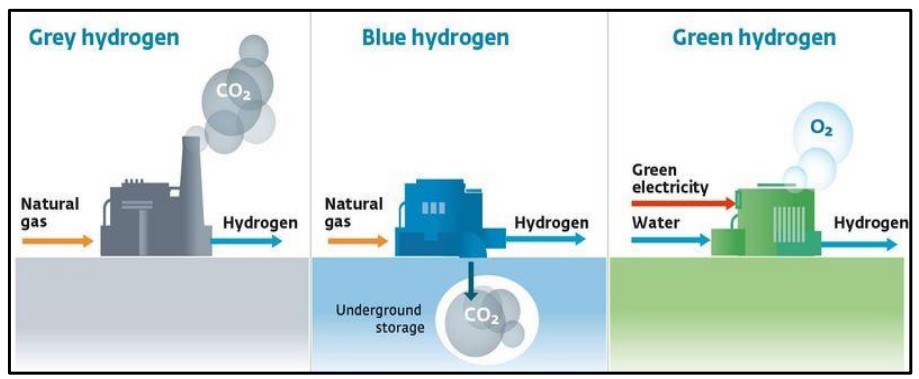
| Grey Hydrogen | Blue Hydrogen | Green Hydrogen |
| It is produced through the decomposition of methane using steam to produce CO2 and H2. | It is produced using the same process which is used to produce grey hydrogen. | It is produced from the decomposition of water using electricity which yields hydrogen and oxygen. |
| Source is either methane or coal. | Source: Methane/coal | Source: Electricity from solar or wind energy. |
| Highest CO2 emissions per unit of hydrogen produced. | Comparatively lower CO2 emissions due presence of technologies to capture large amount of CO2. | Very low or negligible CO2 emissions produced. |
Production Process
Green hydrogen is produced through a process called electrolysis which involves the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen with the help of electricity. This process occurs in a unit called an electrolyzer, which is made up of an anode (positive terminal), the cathode(negative terminal) and an electrolyte.
Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolyzers:
Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Electrolyzers have a solid specialty plastic material as the electrolyte and operate at 70 to 90 Degrees Celsius.
- Anode: Water decomposes to yield oxygen and positively charged hydrogen ions (protons)
- The protons travel from anode to the cathode through the PEM and the electrons move across the external circuit.
- Cathode: Hydrogen gas is formed when hydrogen ions combine with electrons from the external circuit.
- Anode Reaction: 2H2O → O2 + 4H+ + 4e–
- Cathode Reaction: 4H+ + 4e– → 2H2
Alkaline Electrolyzers:
In these electrolyzers, liquid alkaline solution of sodium or potassium hydroxide is used as the electrolyte and the operating temperature is less than 100 Degree Celsius. Hydroxide ions (OH–) travel from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte and hydrogen gas is released at the cathode.
Solid Oxide Electrolyzers:
In these electrolyzers, a solid ceramic material is used as the electrolyte and the operating temperature is 700°–800°C.
How does it works?
- Cathode: Hydrogen gas is formed from the reaction of steam with electrons from the external circuit and negatively charged oxygen ions(O2-).
- Anode: Oxygen gas is produced when oxygen ions react with the anode and generate electrons for the external circuit.
Fuel of the future: Prospects and Challenges
Prospects
- Green Hydrogen is an eco-friendly fuel.
- It is an abundant fuel.
- It is an energy efficient fuel as less quantity of green hydrogen is required to do any work since it has the highest energy content of any common fuel by weight.
- When hydrogen is used in fuel cells, it can run electric vehicles and electronic devices with no need of recharging the fuel cells.
- Green hydrogen can be used in those sectors of the economy which are difficult to decarbonise, such as aviation, shipping, long-distance trucking, and concrete and steel manufacturing, etc.
Challenges
- The highly flammable nature of hydrogen makes it a difficult fuel to handle.
- a. It is difficult to transport hydrogen due to its very low density.
b. Separate pipelines must be constructed to distribute pure hydrogen since hydrogen can cause cracks and weaken the structure of the steel pipes.
3. a. Hydrogen fuel cells are expensive due to the usage of platinum, a highly costly material, as a catalyst in the fuel cells.
b. Green hydrogen production costs are quite high as compared to grey or blue hydrogen since electrolysis is an expensive process.
Global efforts/Programs
- The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) has launched the “Global Programme for Green Hydrogen in Industry”.
- The European Union has launched its new “Hydrogen Strategy” with investments projected to reach 180 billion Euros by 2050.
- South Korea has announced that it will invest trillions of wons in developing electric and hydrogen vehicles.
- The Green Hydrogen Catapult initiative is an initiative launched by the world’s biggest green hydrogen project developers and partners.
- The Hydrogen Council- is sn international organization that aims to promote the use of hydrogen energy all over the world.
National Hydrogen Mission – India
The National Hydrogen Mission was launched in India on its 75th Independence Day, i.e., 15 August 2021. The main goal of this Mission is to ensure that India becomes a global center for the manufacturing of hydrogen and fuel cells technology across the value chain. The Green Hydrogen/Green Ammonia Policy, an integral component of this Mission, aims to increase the production of Green Hydrogen and Green ammonia, i.e., the hydrogen or ammonia which is produced from renewable sources of energy.
Salient features of the Green Hydrogen/Green Ammonia Policy are:
- Green Hydrogen/ammonia manufacturers can buy renewable power from the power exchange or set up their own source of renewable energy.
- Manufacturers can save his or her unconsumed renewable power with a distribution company for up to 30 days and can withdraw it as per the requirement.
- Renewable energy can be supplied to the Green hydrogen/ammonia manufacturers by the distribution licensees after procurement.
Resource Pages
- https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2022/mar/doc202232127201.pdf
- https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1799067#:~:text=Hon’ble%20Prime%20Minister%20launched,India%20a%20green%20hydrogen%20hub.
- Hydrogen Production: ElectrolysisDepartment of Energy
- Green Hydrogen Catapult – Climate Champions (unfccc.int)
- How hydrogen power can help fuel a clean, green recoveryWorld Economic Forum (weforum.org)
- Global Programme on Green Hydrogen in IndustryUNIDO
- Why We Need Green Hydrogen (columbia.edu)
- What is green hydrogen? An expert explains its benefitsWorld Economic Forum (weforum.org)